How to do 3D modeling in AutoCAD?
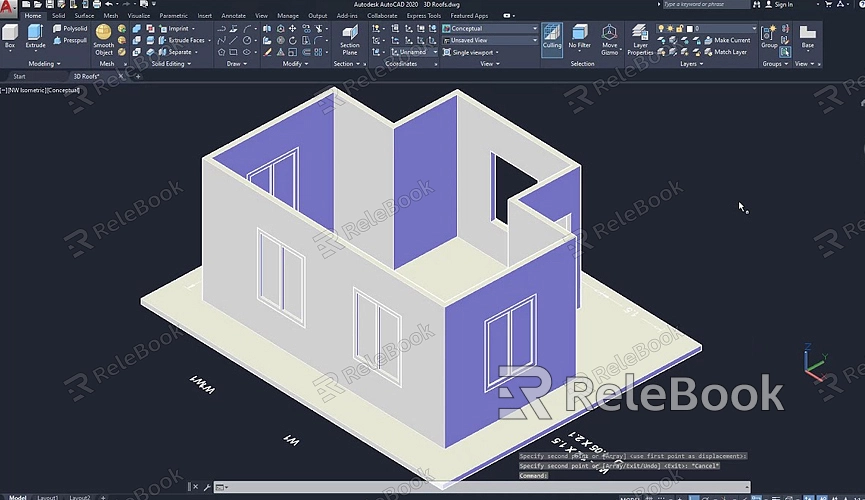
Getting Started with 3D Modeling in AutoCAD
Before diving into 3D modeling, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the AutoCAD interface and workspace setup. Start by opening AutoCAD and selecting the 3D Basics or 3D Modeling workspace from the workspace switcher located at the top-left corner of the screen. This will adjust your interface to show tools and commands pertinent to 3D modeling. Understanding the layout of your workspace is crucial, as it will streamline your workflow and ensure you can easily access the necessary tools.
Creating Basic 3D Shapes
AutoCAD provides a range of basic 3D shapes that can serve as the foundation for more complex models. To create these shapes, go to the “Home” tab and select the “Modeling” panel. Here, you’ll find options such as Box, Cylinder, Sphere, and Cone. Click on one of these options and follow the prompts to specify the dimensions and location of the shape in your drawing area. These basic shapes can be modified and combined to form more intricate designs.
Using 3D Tools and Commands
Once you’ve created your basic shapes, you can begin using various 3D tools and commands to refine and manipulate your model. Key tools include:
Extrude: This command allows you to extend a 2D shape into 3D space, adding depth and volume.
Revolve: Use this tool to create 3D objects by revolving a 2D shape around an axis.
Sweep: The Sweep command creates a 3D object by moving a 2D shape along a specified path.
Loft: Lofting allows you to create complex surfaces by blending between multiple 2D shapes.
To access these commands, go to the “3D Modeling” tab and select the appropriate tool from the “Solids” or “Surfaces” panel. These tools offer a range of options for manipulating your shapes and achieving the desired results.
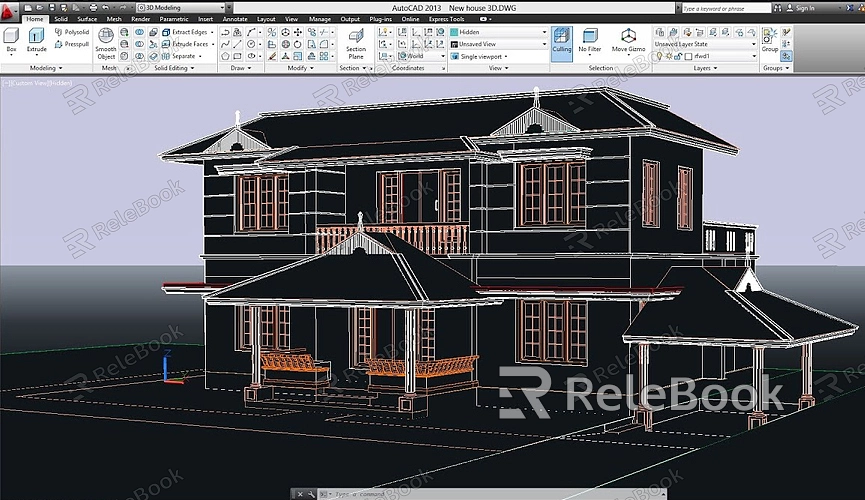
Modifying and Refining Your Model
With your basic shapes in place, it’s time to refine and modify your model to achieve the final design. AutoCAD provides several commands for modifying 3D objects, including:
Union: Combines multiple 3D objects into a single solid.
Subtract: Removes one 3D object from another, creating a cut-out effect.
Intersect: Creates a new object from the overlapping volume of two 3D shapes.
Fillet: Adds rounded edges to your model, which can be useful for smoothing sharp corners.
These commands can be found in the “Solid Editing” panel of the “3D Modeling” tab. Experiment with these tools to see how they affect your model and use them to achieve the desired level of detail and refinement.
Applying Materials and Textures
To enhance the realism of your 3D model, you can apply materials and textures. AutoCAD allows you to assign different materials to various parts of your model, giving them a more realistic appearance. To do this, open the “Materials” panel in the “Visualize” tab and choose from a range of pre-defined materials or create custom ones. Drag and drop the selected material onto your 3D model, and adjust the properties as needed.
Textures can also be applied to add surface detail. Use the “Map” command to assign a texture map to your model, and adjust the mapping coordinates to ensure proper alignment.
Rendering Your Model
Once your model is complete, you may want to create a realistic rendering to visualize how it will look in real life. AutoCAD’s rendering tools allow you to set up lighting, shadows, and camera angles to produce high-quality images of your model. Access the “Render” tab and configure the settings according to your preferences. After setting up your scene, click “Render” to generate a preview image, which you can save and use for presentations or further analysis.
Exporting and Sharing Your 3D Model
Finally, you might need to export your 3D model for use in other applications or for sharing with others. AutoCAD supports a variety of export formats, including DWG, DXF, and STL. To export your model, go to the “Application Menu” and select “Export.” Choose the desired file format and specify the export settings. This will create a file that can be opened in other 3D software or shared with colleagues and clients.
FAQ
What is the difference between AutoCAD 2D and 3D modeling?
AutoCAD 2D modeling focuses on creating flat, two-dimensional designs, while 3D modeling involves creating and manipulating objects in three dimensions, adding depth and volume to your designs.
Can I convert a 2D drawing into a 3D model in AutoCAD?
Yes, you can use tools such as Extrude and Revolve to convert 2D shapes into 3D objects. These tools allow you to add depth and create complex 3D forms from 2D sketches.
How do I improve the quality of my 3D renderings in AutoCAD?
To improve rendering quality, adjust settings such as resolution, lighting, and materials. Ensure that your model is well-defined and use high-quality textures for more realistic results.
What file formats can I use to export my 3D model from AutoCAD?
AutoCAD supports several file formats for exporting 3D models, including DWG, DXF, and STL. Choose the format that best suits your needs based on the intended use of the model.

