How to Create 3D Models of Animal and Plant Cells?
In the study of biology, understanding the structure and function of animal and plant cells is fundamental. A 3D model allows students to visualize and comprehend the complex internal structures of cells more intuitively. Creating a vivid and realistic 3D model of animal and plant cells can greatly enhance learning, be used in educational demonstrations, or support scientific research. This article will explain in detail how to create 3D models of animal and plant cells in 3D modeling software, offering practical tips and methods to achieve this.
Choosing the Right 3D Modeling Software
The first step in creating a 3D model of animal and plant cells is selecting the appropriate 3D modeling software. There are many options available, including Maya, Blender, and 3ds Max, among others. Each software has its strengths; Blender is free and open-source, making it suitable for most users, while Maya is preferred by many professional modelers due to its advanced features and widespread use. Regardless of the software you choose, it should provide sufficient tools and functions to meet the needs of cell modeling.
Once you’ve chosen the software, it’s important to familiarize yourself with its basic operations. Understanding how to create basic geometry, edit vertices, edges, and faces, and apply materials and textures are foundational skills for creating a cell model.
Creating the Basic Structure of the Cell
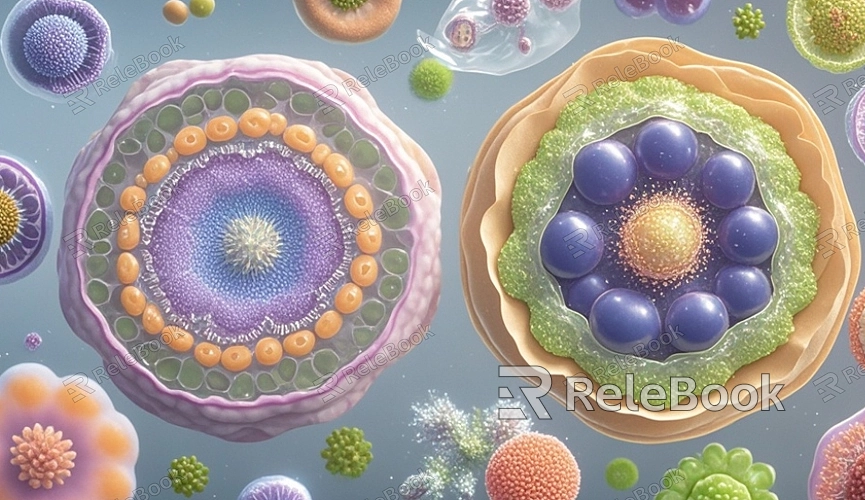
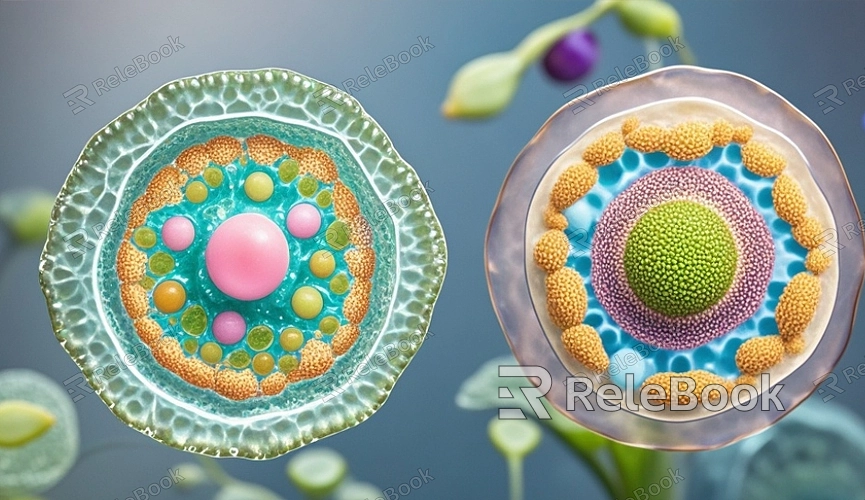
The 3D model of an animal or plant cell typically includes multiple components, such as the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. Start by creating basic geometric shapes. For plant cells, you can use a cube as the base shape for the cell wall since plant cells are usually rectangular. For animal cells, a sphere or ellipsoid is typically used, as animal cells are generally round or irregular in shape.
After creating the basic shapes in the software, you can adjust these geometries by extruding, scaling, and rotating them to match the basic form of the cell structure. The thickness of the cell wall and cell membrane can be achieved through extrusion, ensuring the model’s realism.
Refining the Internal Structure of the Cell
After creating the basic shape of the cell, the next step is refining the internal structure. This part requires accurate reproduction of the internal structures of the cell, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, based on biological knowledge.
First, create a sphere for the nucleus and place it in the center of the cell. Then, use smaller spheres or ellipsoids to represent the nucleolus and place it inside the nucleus. Next, create ellipsoids for the mitochondria and duplicate them to create multiple mitochondria models. The endoplasmic reticulum can be represented by using tubular or flat geometries and arranging them around the nucleus.
During this process, using different colors and materials to distinguish the various organelles is crucial, as it helps the model be more easily recognizable when displayed.
Adding Textures and Materials
To make the 3D model more realistic, it is essential to add appropriate textures and materials. Textures can depict the softness of the cell membrane, the rigidity of the cell wall, and the complex structure of the mitochondria.
In 3D modeling software, you can apply different materials to each organelle. For example, you can apply a semi-transparent material to the cell membrane to represent its semi-permeability and apply a textured material to the mitochondria to highlight the differences in structure between the inner and outer membranes. During this process, you can use the UV unwrapping function to unfold the model’s surface into UV maps, which can then be detailed using drawing software like Photoshop or Substance Painter.
Additionally, proper lighting settings can enhance the model’s presentation. By adjusting the direction and intensity of light sources, you can highlight the model’s depth and detail, giving it greater visual impact.
Optimizing and Rendering the Model
After completing the model, it’s essential to optimize it to ensure smooth display across different devices or software. This includes reducing unnecessary vertices and polygons, checking the model’s normals, and optimizing the UV layout. Additionally, you can enhance the final presentation of the model by adding appropriate backgrounds and lighting effects.
Rendering is the final step in showcasing the 3D model. Through rendering, you can generate high-quality still images or animations to display different angles and structural details of the cell. Depending on your needs, you can adjust parameters such as shadows, reflections, and refractions during rendering to achieve the best visual effect.
Creating 3D models of animal and plant cells is a process that combines biology with 3D artistry. Through careful design and detailed production, you can create scientifically accurate and visually stunning models. This not only helps to better understand cell structures but also serves as a valuable tool for education and research. After mastering these techniques, it’s recommended to download more high-quality 3D models and textures from the Relebook website to enrich your creative resources.
FAQ
Why does my cell model not look realistic enough?
This might be due to a lack of detail or improper material settings. Enhancing the details of the organelles, using high-quality texture maps, and adjusting the glossiness and transparency of materials can improve the model’s realism.
How can I add more depth to my cell model?
You can add depth by adjusting the position and intensity of the light sources to increase shadow effects on the model or by adding normal maps and displacement maps to the materials to enhance the cell surface’s fine details.
Why does my UV map appear stretched on the model?
This occurs when the UV layout has not been sufficiently optimized. You can manually adjust the scale and position of UV islands in the UV editor to ensure that each part of the UV map has a consistent scale, preventing stretching issues.
Can I add animations to my cell model?
Yes, most 3D modeling software supports animation. You can add rotation, movement, or other animation effects to the organelles or simulate biological processes like cell division and substance transport.
How do I export my 3D cell model?
After completing modeling and rendering, you can export the model in common 3D formats such as OBJ or FBX. This allows you to continue editing in other software or use it directly for display.

