How to Make a 3D Model of the Lungs
Creating a 3D model of the lungs is an engaging and challenging task, especially valuable in medical and educational contexts. Whether for research, teaching, or visual effects, a high-quality 3D lung model can help you better understand and showcase the structure and function of the lungs. This guide will walk you through the process of creating a detailed 3D lung model, including modeling, texturing, material setup, and rendering.
Planning and Preparation
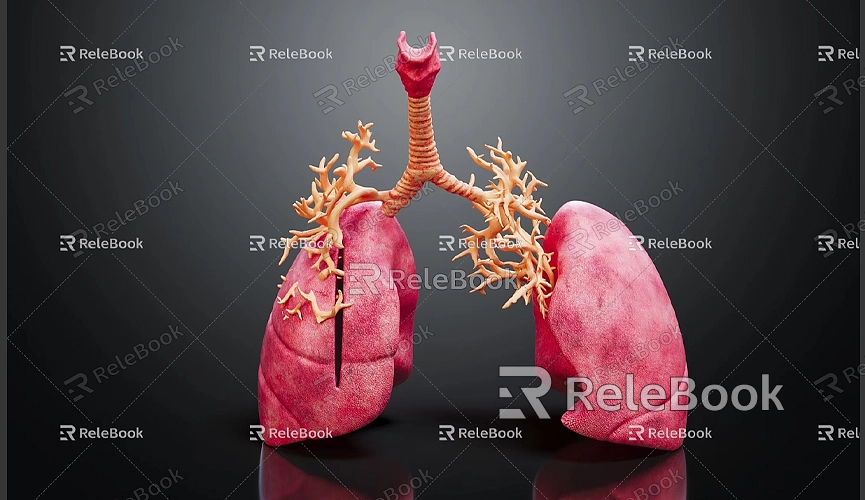
Before you start modeling, thorough planning and preparation are essential to ensure a smooth workflow.
1. Gather Reference Materials:
- Find anatomical references and medical images of the lungs. These can be obtained from medical textbooks, online databases, or anatomy websites. Reference images will help you accurately reproduce the details of the lungs.
- Obtain CT scans or 3D anatomical images of the lungs, which are invaluable for creating a model with rich detail.
2. Choose Modeling Software:
- Select suitable 3D modeling software for the task. Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max are excellent choices. This guide will use Blender as an example, but the methods described are applicable to other modeling software as well.
Creating the Lung Model
To create a lung model in Blender, follow these steps:
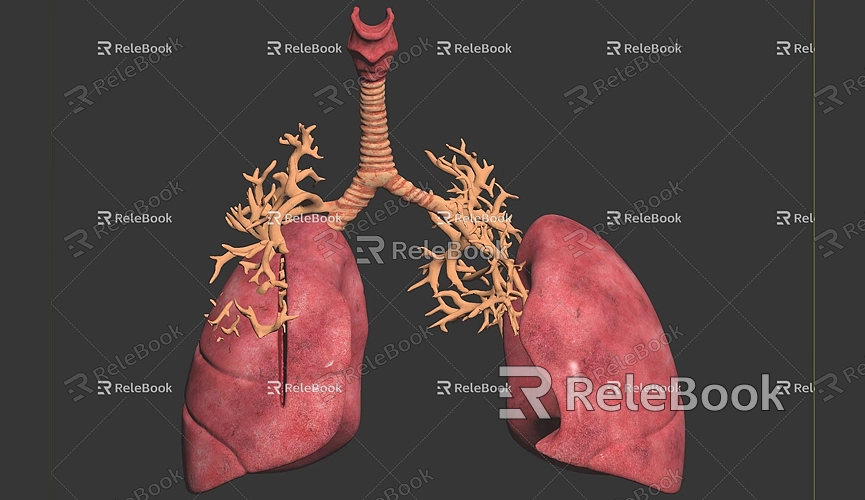
1. Create the Base Geometry:
- Start Blender and create a new project. In the "Create" menu, select "UV Sphere" as the base shape for the lungs.
- Enter "Edit Mode" to modify the sphere’s shape to resemble the lungs. Since the lung shape is asymmetric, you will need to model the left and right lungs separately.
2. Detail Sculpting:
- Use "Sculpt Mode" to add details such as the bronchial branches and alveoli. Blender's sculpting tools are ideal for creating complex details.
- To enhance the model's realism, use the "Displacement Modifier" to create subtle surface variations and textures.
Adding Textures and Materials
Texturing and material setup are crucial for enhancing the model’s realism. Here’s how to add textures and materials to the lung model:
1. UV Unwrapping:
- Enter "UV Editing" mode to unwrap the model’s UVs. UV unwrapping maps the 3D model’s surface to a 2D texture image. Ensure there are no overlaps and minimize seams to avoid texture distortion.
2. Apply Textures:
- Create textures for the lung model in Blender. You can use medical images as a basis for your textures or paint textures to simulate the surface features of the lungs.
- For high-quality 3D textures and HDRIs, you can download free resources from [Relebook’s texture site](https://textures.relebook.com/). This site offers a range of high-quality resources to enhance the realism of your lung model.
3. Set Up Materials:
- Create and apply materials to the lung model. Adjust the material’s color, glossiness, and transparency to match the realistic appearance of lung tissue.
- Use Blender’s node editor to create more complex material effects, such as semi-translucent lung tissue and subtle glossiness.
Setting Up Lighting and Camera
Proper lighting and camera setup are crucial for showcasing the details of your lung model. Here’s how to configure lighting and camera:
1. Configure Lighting:
- Add light sources to illuminate the model. You can use "Point Light" or "Area Light," adjusting their intensity and position to simulate natural light.
- Consider using HDRI (High Dynamic Range Imaging) as an environment light source for more even and realistic lighting.
2. Set Up the Camera:
- Add a camera and position it to capture the best view of the lung model.
- Adjust the camera’s focal length and depth of field settings to add depth and dimension to the image.
Rendering the Model
Rendering converts the 3D model into a 2D image and requires careful setup. Follow these steps to render your lung model:
1. Select a Rendering Engine:
- In Blender, choose between Eevee or Cycles rendering engines. Eevee is suitable for real-time preview and faster rendering, while Cycles provides higher quality render results.
- Select the appropriate rendering engine based on your needs and adjust the settings accordingly.
2. Adjust Render Settings:
- In the "Render" panel, set parameters such as resolution, anti-aliasing, and sampling rate. Increasing the sampling rate improves image quality but extends rendering time.
- Configure other settings like ray tracing and shadow quality to optimize the final render.
3. Execute the Render:
- Click the "Render" button to start rendering the lung model. Once rendering is complete, save the image in PNG or JPEG format for display or further processing.
Creating a 3D model of the lungs involves a detailed process, from basic modeling and texturing to material setup and final rendering. Using 3D modeling software like Blender, you can create a detailed and realistic lung model that highlights its structure and function.
For high-quality 3D models, you can download from [Relebook’s model site](https://3dmodels.relebook.com/). Relebook offers a wealth of premium 3D resources. If you need high-quality textures and HDRIs for your models and scenes, visit [Relebook’s texture site](https://textures.relebook.com/) for free downloads. These resources will help you enhance the quality of your model and achieve more realistic results. I hope this information helps you in creating your lung model.

