How to Create 3D Texture Maps
3D texture maps are essential for enhancing the details of models and directly influence the realism and quality of rendered scenes. From simple game assets to complex architectural visualizations, texture maps are indispensable for any 3D artist. Tools like Blender, 3ds Max, and Maya offer robust texture mapping features, while software like Photoshop and Substance Painter excels at editing and refining textures. This guide will walk you through the core concepts and practical techniques of creating 3D texture maps, enabling you to improve your workflow and achieve professional results.
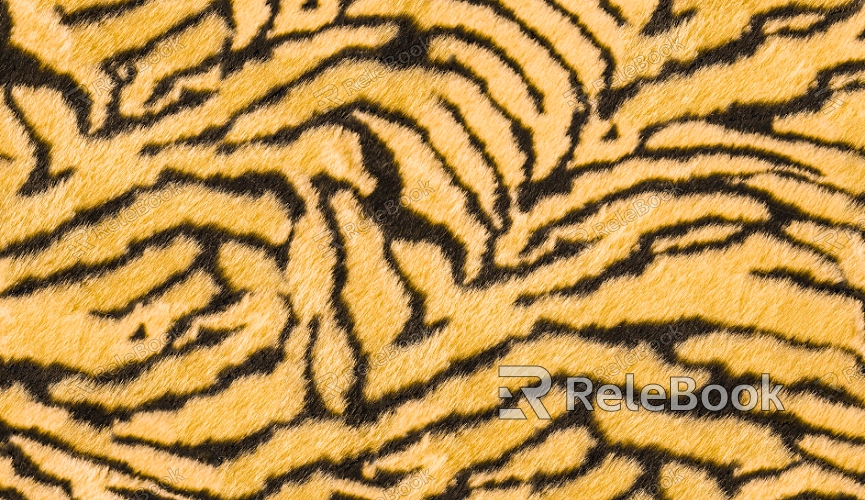

1. Understanding Types of Texture Maps and Their Functions
Before diving into the creation process, it’s crucial to understand the different types of texture maps and their purposes.
Common Types:
Diffuse Maps: Define the base color and patterns of an object.
Normal Maps: Simulate surface details such as bumps and fine textures without adding polygons.
Glossiness and Metalness Maps: Control an object’s reflectivity and metallic properties.
Ambient Occlusion Maps: Add subtle shadow details to enhance realism.
Real-World Applications:
In game design, normal maps reduce the need for high polygon counts.
In architectural rendering, combining diffuse and ambient occlusion maps enhances the intricacy of details.
2. Preparing UV Mapping
UV mapping is a critical step that determines how textures are applied to your model's surface.
Importance of UV Mapping:
Properly unwrapped UVs ensure textures are not stretched or distorted and are distributed evenly across important areas.
Optimizing UV Layouts:
Automatic Tools: Use features like Blender's Smart UV Unwrap for quick and effective layouts.
Manual Adjustments: For complex models, refine edges and seams to avoid overlapping textures.
3. Gathering and Creating Texture Resources
High-quality resources form the foundation of compelling texture maps.
Capturing Real-World Textures:
Use high-resolution cameras to photograph surfaces like wood, stone, or fabric. These images can be edited and used directly as textures.
Utilizing Online Libraries:
Platforms like Polyhaven and Textures.com offer free and premium high-quality textures.
Generating Custom Textures:
Leverage tools like Substance Designer to create seamless, customizable textures tailored to your project.
4. Crafting Custom Texture Maps
Creating custom textures offers unmatched flexibility, making it ideal for unique projects.
Using Specialized Tools:
Substance Painter allows for real-time painting directly on 3D models.
Photoshop is excellent for intricate detail work on texture maps.
Layering Details:
Build multi-level effects by adding dirt, scratches, and natural wear to make textures more dynamic and realistic.
Combining Brushes and Filters:
Use specialty brushes for specific surface details and apply filters to fine-tune contrast and saturation.
5. Creating Seamless Textures
Seamless textures are essential for covering large areas without visible edges or patterns.
Automatic Tiling:
Software like GIMP and Photoshop offers built-in features to quickly generate seamless textures.
Manual Edge Refinement:
When automatic methods fall short, use tools like the clone stamp and gradient fills to smooth transitions manually.
6. Fine-Tuning Texture Parameters
Once a texture map is applied, adjust its parameters to suit the model and the scene.
Testing Material Appearance:
Preview renders to ensure the texture’s color and details match the desired look.
Adjusting Reflectivity and Roughness:
With PBR workflows, tweak glossiness and reflectivity settings for optimal material realism.
Ensuring Color Consistency:
Use Photoshop to correct tone and color, ensuring cohesion with other assets in the scene.
7. Optimizing Texture Files
Well-optimized texture files improve rendering efficiency and save storage space.
Choosing the Right Format:
PNG is suitable for high-quality textures with transparency.
JPG works well for projects that prioritize smaller file sizes.
Compressing File Size:
Tools like TinyPNG can reduce file sizes without noticeable quality loss.
Organizing and Naming Files:
Use a clear naming convention and categorize textures for easier retrieval during future projects.
By following these steps, you’ll gain a solid understanding of how to create effective 3D texture maps. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced designer, these techniques can significantly enhance your models’ visual quality and realism.
Looking for high-quality 3D texture resources or support for SketchUp models and 3ds Max files? Relebook is the perfect destination. Explore Relebook to access a wide range of assets and bring your projects to life with ease and creativity!

